Where Craftsmanship Meets Nature
Explore the world of log homes in 100 Mile House and the Cariboo region. From rustic cabins to grand timber estates, discover inspiring stories, expert insights, and practical guides for log home enthusiasts.
Explore Log Home Living
Browse our collection of articles covering every aspect of timber home ownership
Deco
Interior decoration and trends
Equipment
Equipment and appliances
Garden
Gardening, plants and outdoors
House
Home maintenance and living
House moving
Moving tips and organization
News
Home and housing news
Real estate
Property, buying and renting
Swimming pool
Pools, spas and maintenance
Works
Renovation and DIY projects
What Our Readers Say
Stories from log home enthusiasts across the region
This site has been invaluable for understanding log home maintenance. The seasonal guides helped me prepare my cabin for winter, and the restoration articles gave me the confidence to tackle my own projects.
As someone planning to build a log home, these articles have been my go-to resource. The detailed features on different wood types and construction methods helped me make informed decisions for my project.
I love the real estate features showcasing beautiful timber homes in the area. The photography is stunning and the detailed descriptions give great insight into what makes each property special.
Latest articles
Our recent publications


Essential indoor plants for air purification in low-light uk apartments

Innovative ideas for crafting a space-saving outdoor kitchen in your uk home

Unlocking Biodiversity: A Guide to Cultivating Heritage Apple Varieties from the UK

Revitalize your workspace: key design strategies to boost productivity in your uk home office

Build your own solar dehydrator: a comprehensive guide to preserving the bounty of your uk garden harvest

Mastering indoor hydroponics in the uk: your ultimate handbook for abundant herbal harvests

Maximize comfort: innovative entryway strategies for uk homeowners to minimize heat loss

Elevate your home"s security: the ultimate uk homeowner"s guide to smart locks and video doorbells

Effective draught-proofing techniques to boost energy efficiency in iconic uk period properties

Top Materials for Crafting a Stunning and Long-Lasting Garden Path in the UK

Top Herbs to Cultivate on Your UK Kitchen Windowsill for Fresh Flavours

Transform Your Urban UK Garden into a Canine Paradise: Top Tips for Dog-Friendly Design
Discover vintage steampunk lamps that exude unique elegance

Luxurious interior design in monaco: personalized & elegant spaces

Save big with exclusive laser engraver coupon codes inside!

Unlock incredible savings: top laser engraver coupon offers!

Cost breakdown: diy moving vs. hiring expert movers in bristol – what's your best option?

Unlocking convenience: top strategies for negotiating stair and elevator access in uk apartment buildings

Farmingdale observer: essential insights for your indoor garden

Ultimate 2023 playbook for uk homeowners: unlocking grants for asbestos removal

Vital 2023 insights for uk employers: mastering maternity and paternity leave regulations

Your ultimate 2023 handbook: a step-by-step approach for uk residents to claim a community garden plot!

Assessing the consequences of building near norfolk"s wildlife conservation areas: a deep dive

Crucial tax considerations for uk property inheritance: key information you must be aware of

Ultimate checklist for assessing property energy efficiency before purchasing in scotland
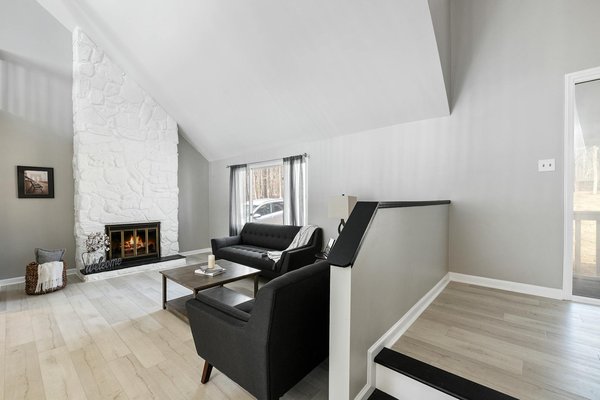

Enhancing indoor pool acoustics: creative strategies for a tranquil aquatic sound experience in your uk home
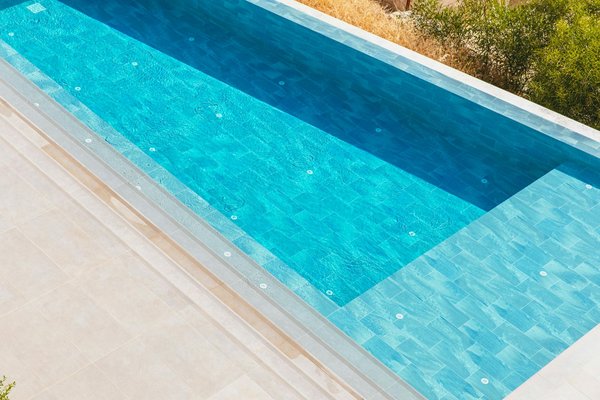

Top strategies to reduce water loss in your uk home swimming pool
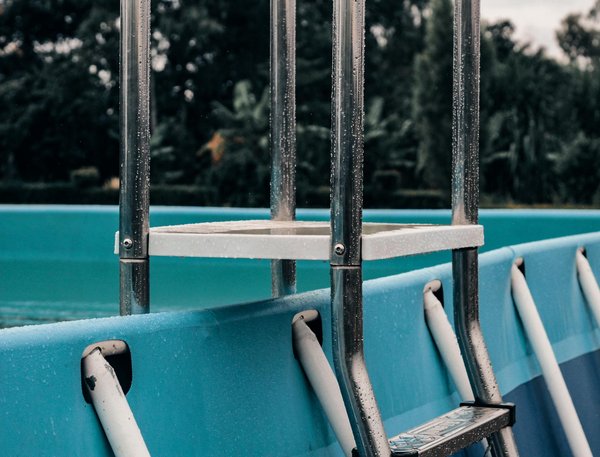

Transform your uk swimming pool: boost water quality naturally with aquatic plants
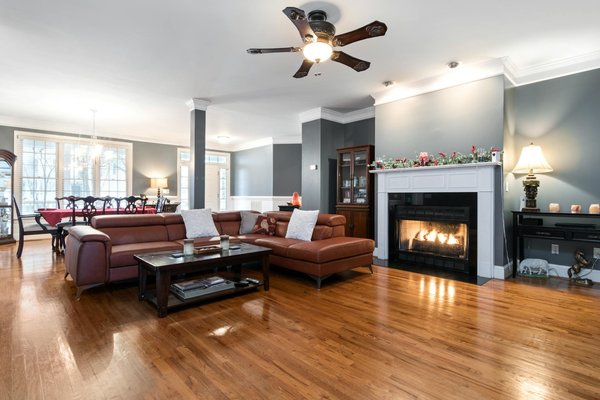

Comprehensive guide to eco-friendly wool carpet installation in your brighton residence
Crafting Your Perfect Log Home Retreat
Experience the authentic charm of handcrafted log homes nestled in the heart of British Columbia's Cariboo region. Our skilled artisans work alongside renowned specialists like ebenisterie-noircler.com to create bespoke interiors that complement the natural beauty of your log home. From rustic charm to modern comfort, we bring your vision of sustainable living to life.
- Sustainable timber construction
- Custom interior design solutions
- Authentic Cariboo craftsmanship


